Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases of the spine. It usually appears in many people over the age of forty, but it often occurs in younger people. Osteochondrosis is included in the ICD-10, its code is M42 (codes M40-M43 - deforming dorsopathy)
Osteochondrosis is a stratification of the intervertebral discs, due to which they become flatter and reduce the overall height of the spinal column. Deformed intervertebral discs lead to pinched nerves and pain. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is relatively rare, since it is this area, consisting of 12 vertebrae, that is well fixed by the ribs and sternum. The disease usually affects the upper vertebrae of the department.
Causes of thoracic osteochondrosis
This disease most often appears in people in whose family cases of osteochondrosis are frequent, but there are exceptions. The appearance of the disease can lead to:
- congenital pathologies of the spine;
- trauma;
- constant strong physical activity;
- serious metabolic disorders;
- general muscle weakness;
- infections and frequent temperature changes;
- constant stress.
Osteochondrosis appears in many women during menopause.
Signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Symptoms of this disease can be different, much depends on the age of the patient, the degree of the disease and the stage. During remission, the disease can be practically not felt, but during an exacerbation it is impossible not to notice it.
Pathological changes in the spine manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- sharp or aching pain in the chest, in the region of the spinal column (dorsago);
- if the nerve roots that come out of the spinal cord (radiculopathy) are damaged, shooting pains, paresthesias and various sensory disturbances appear;
- there is aching pain in the region of the heart, which does not disappear after taking glycerol trinitrate;
- pulmonary syndrome, which can be identified by signs of oxygen starvation and poor ventilation;
- acute pain in the abdomen;
- pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is not accompanied by fever, as is often the case with back pain;
- pain syndrome increases with pressure on the vertebrae;
- compressive myelopathy may develop. Myelopathy is characterized by a change in the sensitivity of the skin and muscles near the affected area of the spine.
Important!Osteochondrosis of the thoracic and lumbar regions often simulate diseases of the internal organs. Patients may experience pain in the stomach, liver, heart due to pinched nerves. Over time, "perceived" illnesses may actually appear due to persistent inflammation.
If the patient feels pain in the internal organs, but pain is the only symptom, it is necessary to check the condition of the spine. So, for example, the tenth vertebra is responsible for the innervation of the kidneys and the general condition of the body. With his osteochondrosis, a person feels pain in the kidneys, quickly gets tired. That is why it is important not to self-medicate, as is often advised in various forums, but to consult a specialist.
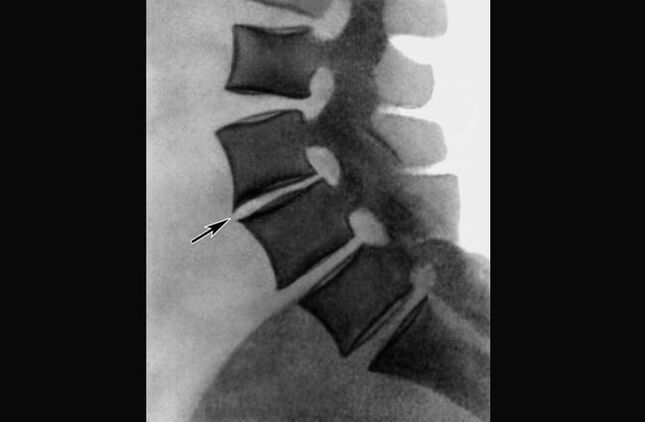
Stages of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
The international classification has established 4 stages (degrees) of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, each of which has its own clinical picture:
1 degree.At this stage, the disease only arises as a result of the fact that the intervertebral disc loses moisture, its height decreases, the vertebrae approach each other and begin to compress the nerves. The patient may feel a local pain syndrome in the region of the diseased vertebra, occasionally there are characteristic backaches. Painful sensations occur with active movement and physical exertion, but some exercises can relieve discomfort. Usually, the 1st degree of the disease is taken for ordinary fatigue, so people do not rush to the doctor.
2 degree.The vertebra loses stability, and cracks form on the annulus fibrosus. Due to the increase in instability, both obvious and hidden subluxations are possible, which in the future can bring a lot of trouble. The patient experiences pain not only during physical exertion, but sometimes in a stationary state (for example, lying on his side or back). Osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree is also characterized by general weakness, increased fatigue, pain can be observed in the area of \u200b\u200bthe internal organs, in the limbs. Thoracalgia may occur.
3 degree.The fibrous ring becomes thinner, it ruptures, which causes a herniated disc. Such a disease causes a number of deviations in the work of internal organs, since the spine is in a curved state and severely restricts movement, forcing a person to take positions in which pain is felt less. The pain syndrome is very strong, at this stage the formation of the spine with radicular syndrome is possible.
4 degree.The vertebrae begin to grow in width, their processes ossify, and the remnants of the intervertebral discs also ossify. Patients often note a decrease in pain, but the mobility of the spinal column also decreases markedly. The vertebrae approach each other, ossify and grow their roots, which reduces the depreciation capacity of the spine. A person with advanced osteochondrosis noticeably loses height, his movements become constrained, spinal curvature (kyphosis or lordosis) is observed.
Against the background of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, various diseases of the internal organs can form, so it is dangerous to delay diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostic methods
The main radiological signs of this disease are:
- Irregular contour of the intervertebral disc;
- Wavy edge of integumentary plates;
- Hook-shaped processes are enlarged and pointed;
- Reduced height of intervertebral discs;
- Changed the shape of the intervertebral discs;
- Herniated intervertebral discs (it is easier to determine the anterior hernias);
- Occurrence of osteophytes;
- The shape of the vertebral body is changed.
In certain cases, an x-ray contrast study is performed - discography, which shows the following features:
- Irregular contour of the nucleus pulposus;
- In the severe phase of the disease, the intervertebral disc is completely filled with contrast;
- With a significant destruction of the disc, a contrast is observed that goes beyond its limits, sometimes falling into the spinal canal.
Consequences of osteochondrosis
If the disease is not treated, then its progress is very rapid. But with successful treatment, the number of possible complications is minimal. There are several main complications of osteochondrosis:
- Sciatica
- Spondylosis of the thoracic spine (and other departments)
- VSD
- Decreased hearing or vision
- Radiculitis
- Migraine
- Lumbago
- Intervertebral rufous
- Spondylarthrosis
- Disability
- Thoracalgia
- Epicondylitis
The main methods of treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Now the treatment of osteochondrosis of the chest is carried out using the following methods:
- Conservative treatment
- Surgical treatment
- traction
Medical treatment is based on several principles. The main one is the fight against pain, as well as the reduction of inflammation. Thus, doctors use anti-inflammatory drugs in order to eliminate pain.
To improve the condition of cartilage, doctors prescribe prescription chondroprotectors to patients.
Often, restrictions in the movement of the spine are caused by highly stretched muscles. In order to get rid of this disease, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants and antispasmodics.
To reduce pain, doctors recommend that patients use various ointments for osteochondrosis, which produce a warming effect.
To effectively treat this disease, a controlled dosage of the drug by a doctor is important. The patient must remember that it is necessary to take medicines strictly in the order that was indicated by the doctor. Mixing drugs or replacing them with analogues should not occur without the consent of the attending physician.
In addition to medical treatment, doctors prescribe acupuncture, reflexology, physiotherapy, therapeutic massage. All of these treatments should be discussed in detail with your doctor and must be performed by a professional.
In the early phases of the disease, the entire treatment process of osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine is limited to physiotherapy exercises for osteochondrosis and several special exercises. Drug therapy consists of prescribing drugs that improve metabolism, as well as vitamin therapy.
Patients are advised not to do gymnastics without discussing this with their doctor. It should be noted that in the acute phase of the disease, no gymnastics can be done. Any exercise therapy is selected depending on the location of the damaged area in the spine. Folk remedies can also be used.
What to do with an exacerbation of the disease?
Exacerbation of osteochondrosis is always accompanied by pain. Thus, the main treatment is aimed at reducing pain.
For this, NSAIDs are prescribed. They reduce the generation of prostaglandins, which irritate the nerve endings responsible for pain. In cases of ineffectiveness of these drugs, blockade with local anesthetics can be used. Also, during an exacerbation of the disease, heavy physical exertion should be avoided, rest is recommended. Therefore, in such situations, exercise with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is contraindicated until further decision by the attending physician.

Prevention measures
In order to prevent the development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, you should always take care of your health.
The first step is to eliminate all factors that can provoke the formation of osteochondrosis, do not forget about the danger of heavy physical exertion, and maintain correct posture.
Each person should undergo regular examinations in a specialized dispensary. If, during a medical examination, the doctor found primary pathologies of the spine, the patient should immediately contact an orthopedist.
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to treat all diseases in a timely manner, and this is especially important in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. After injuries, it is necessary to undergo mandatory rehabilitation.
Take care of your body: change the position of your body more often during work to avoid hypothermia and hyperthermia, do not forget about medical examinations.
At home, people cannot always keep their body in the right tone, as can be done in the gym. But still, do not forget to strengthen your back muscles with various exercises. So, for example, physiotherapy exercises for osteochondrosis will help very well. The main thing is not to overdo it. And photos and videos of exercises are easy to find on the Internet.
The best prevention of any disease is a balanced diet. Your diet should contain not only vegetables, but also a complex of vitamins, which is especially important in the spring-winter period. In order to strengthen the back, you can use massage, medicine, swimming.


























